GlosArch has an active fieldwork programme. We perform geophysical surveys of sites of potential archaeological intertest using resistivity and magnetometry to look beneath the ground and we undertake archaeological excavations at sites brought to our attention by members. No prior experience is required to take part in either of these activities and training and equipment are available to borrow. We also study sites and landscapes using publicly available resources, including historic maps, aerial photographs and LIDAR.
For details of forthcoming activities please see the Home page.


Geophysical Surveys
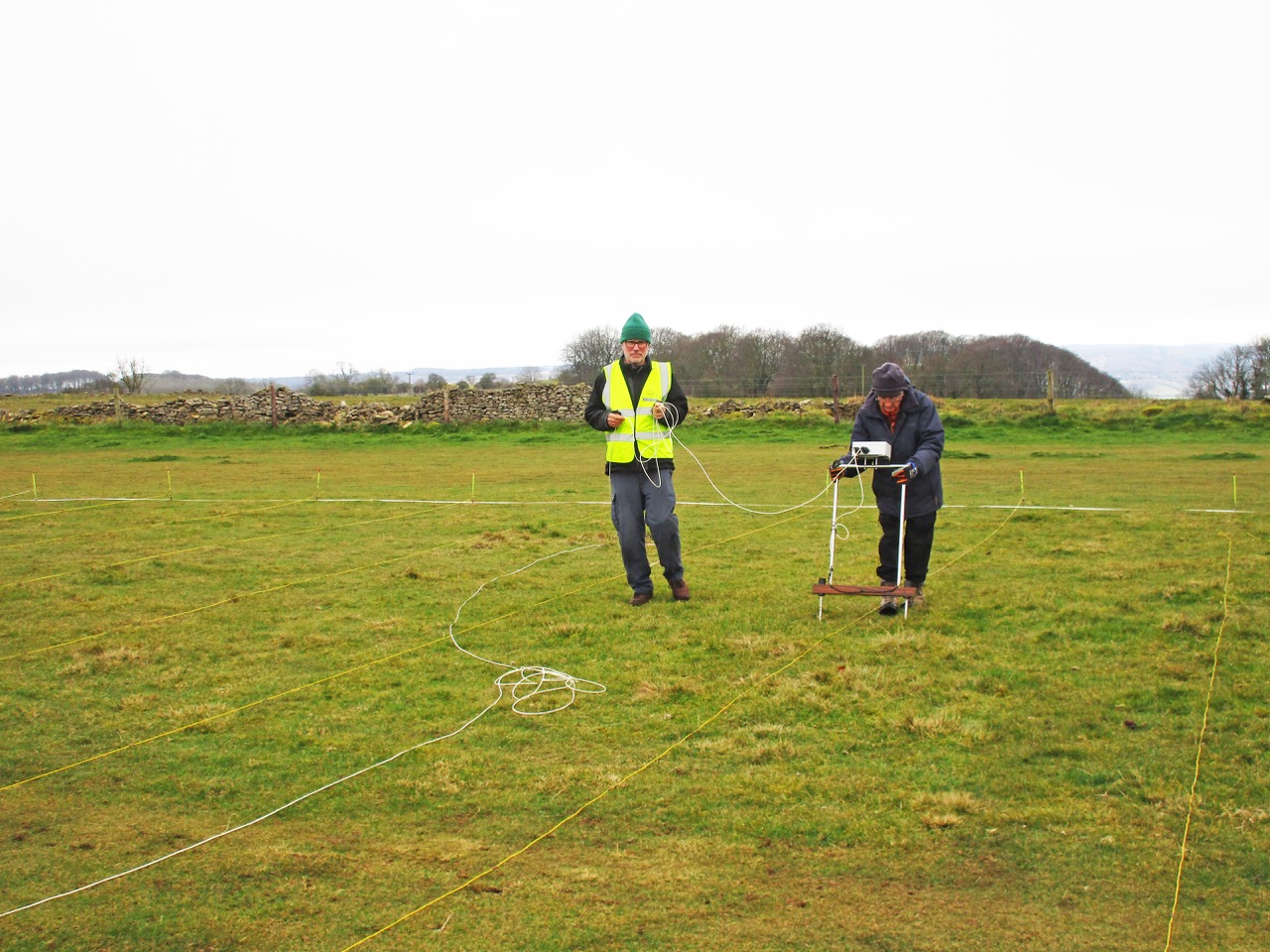
Resistivity surveying measures changes in the ground resistance to a current passed between a pair of reference electrodes and a pair of sensing electrodes, caused by archaeological features beneath the ground. Solid objects, such as buried foundations or paths, result in higher resistance, whilst cut features such as ditches result in lower resistance. Readings are taken at regular intervals over a series of 20mx20m grids and the values are used to create a two-dimensional image of what is under the ground using computer software. GlosArch owns a TR/CIA resistivity meter.
Recent surveys have been undertaken a on Cleeve Hill at the site of the grandstand of the first racecourse, at the hillfort and The Ring on Cleeve Common, and ahead of excavations at Brookthorpe and Minsterworth. Further work is planned on Cleeve Hill.
Magnetometry, as the name suggests, uses tiny variations in the earth’s magnetic field to identify archaeological features beneath the ground. Disturbance of the ground, for example by a filled-in ditch, changes the orientation of magnetic particles in the ground relative to the earth’s natural field and can be detected by the magnetometer. As with resistivity surveying, readings are taken at regular intervals over a series of 20x20m grid squares and the measurements are converted to an image of the site using computer software. GlosArch recently purchased a Frobisher DFG-1 magnetic gradiometer.
Recent surveys have taken place at Brookthorpe and at the Cleeve Common hillfort. Future work is planned at some other potentially interesting sites on Cleeve Hill as well as extending the survey at Brookthorpe and surveying some features at Castlemeads on Alney Island opposite Gloucester prison.
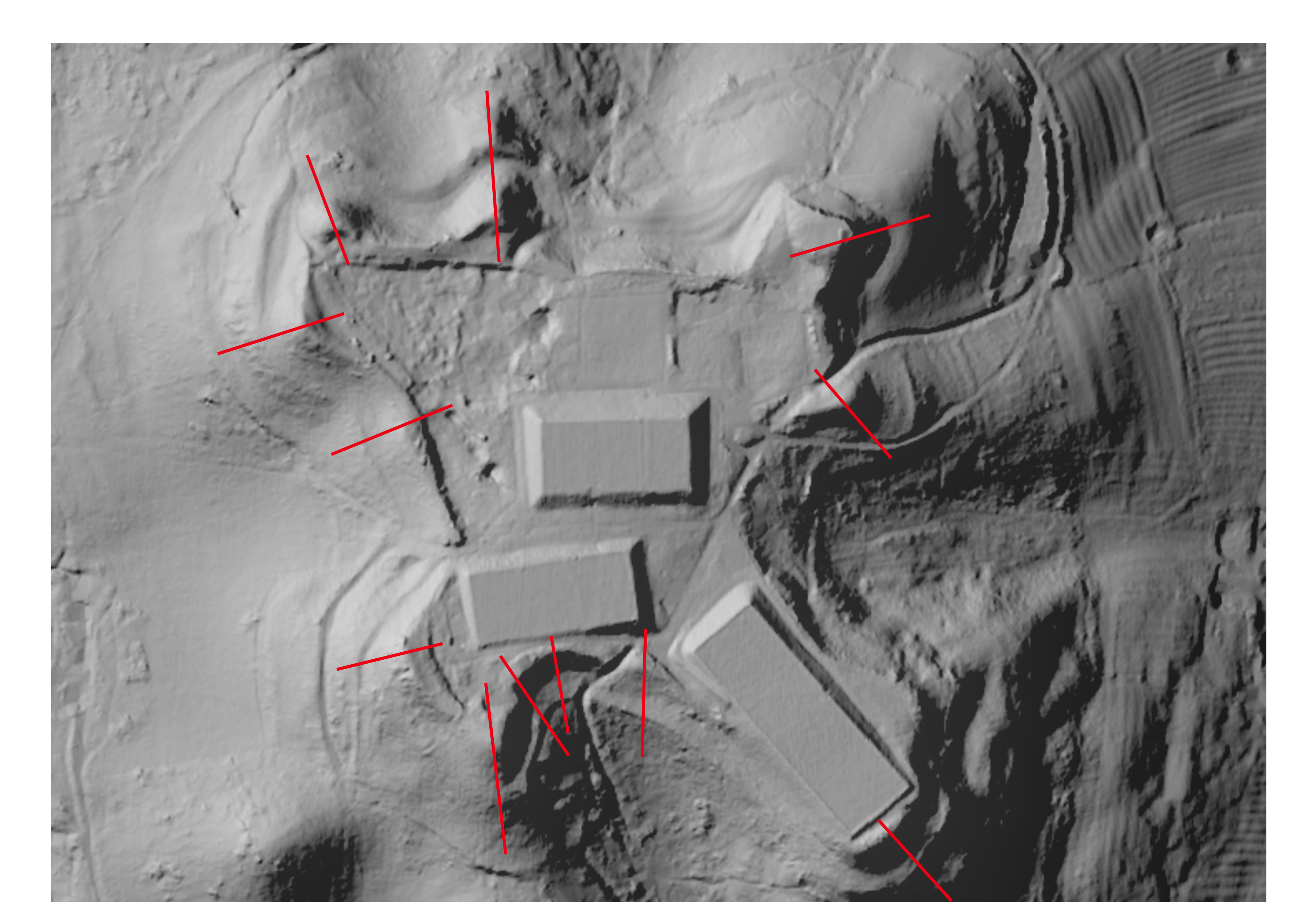
Cleeve Hill – Cheltenham’s first racecourse.
Following our successful identification last year of the second grandstand of the original Cheltenham racecourse, which was active from 1819 until the 1840’s, we have recently undertaken a magnetometry survey to try to locate the first grandstand, that was burnt down, probably as a result of arson, in 1829. No clear evidence of this wooden structure has been detected to date. The work generated quite a lot of media interest with an interview on BBC Points West and a report in The Racing Post.
For details of the recent excavation at this site, see below.
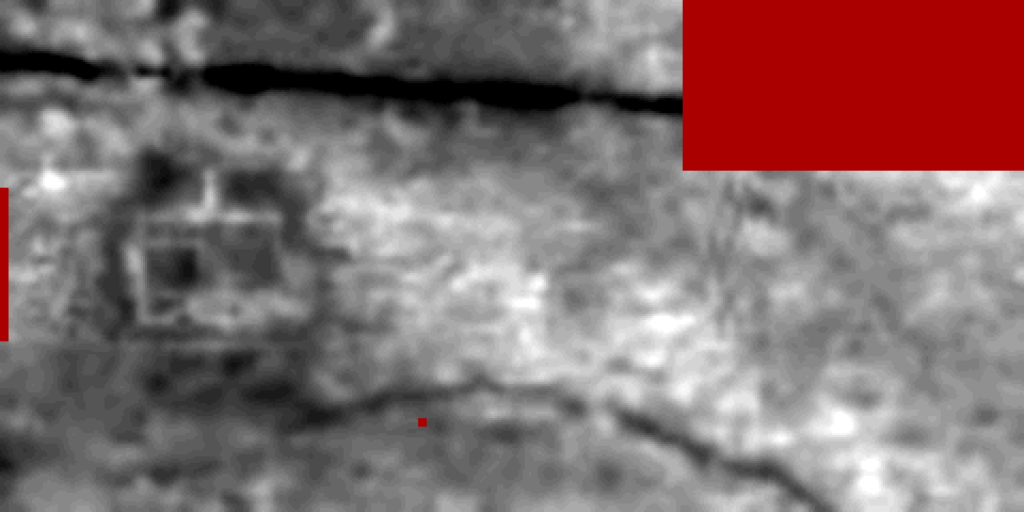
Castlemeads, Gloucester
Following the magnetometer survey of Castlemeads late last year, thanks to a collaboration with Exeter University, who lent us the kit, we have now undertaken a ground penetrating radar survey of the site. This was a joint activity between GlosArch members and Exeter University students. Initial processing of the results confirms the route of the electric cables seen in the magnetometry survey and demonstrates solid archaeology, in a similar pattern to the LIDAR features, a short way beneath the surface as well as some enigmatic deep features towards the river.
If you would like to take part in future work please email: fieldwork@glosarch.org.uk Please note no previous fieldwork experience is required to take part.
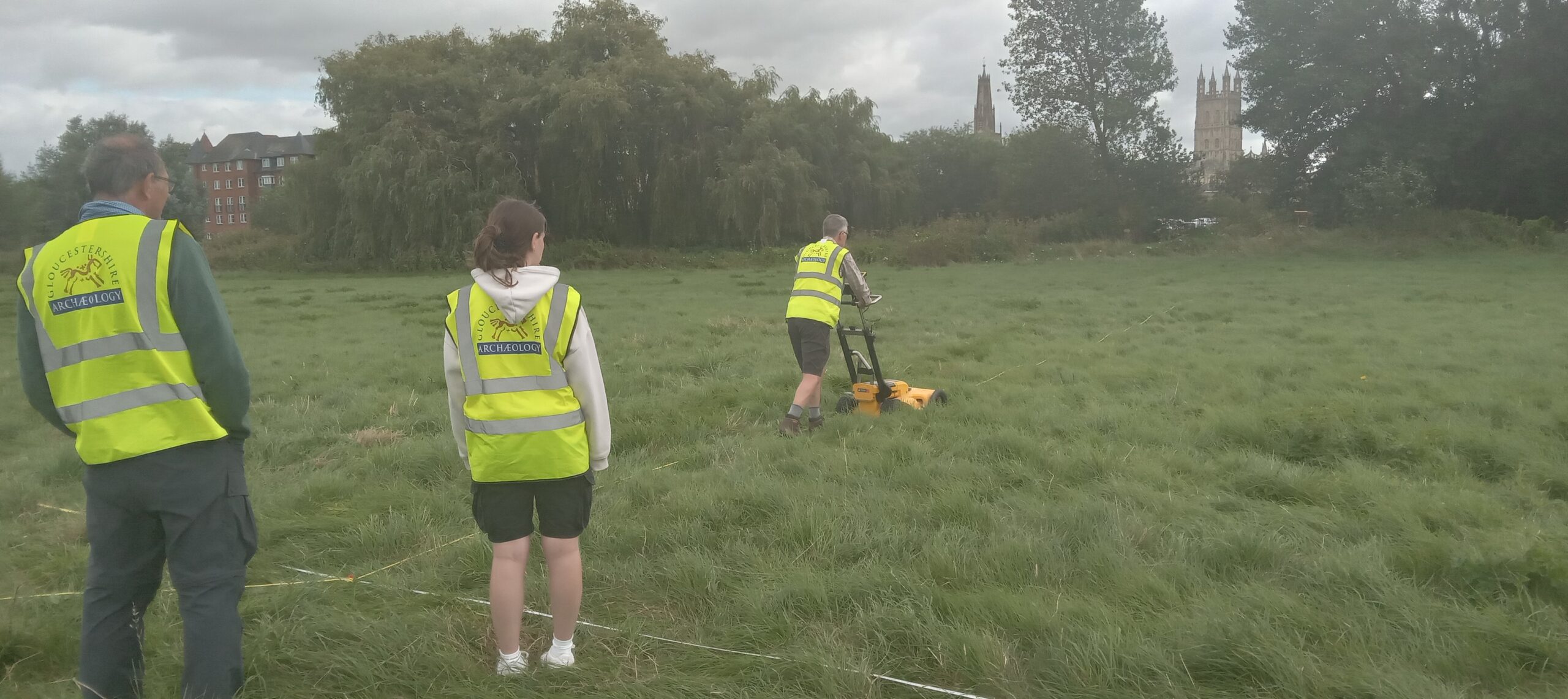

Forthcoming Geophysical Surveys
Keep checking here for information on future geophysical surveys.
Current Excavations
Cleeve Hill – Cheltenham’s first racecourse.
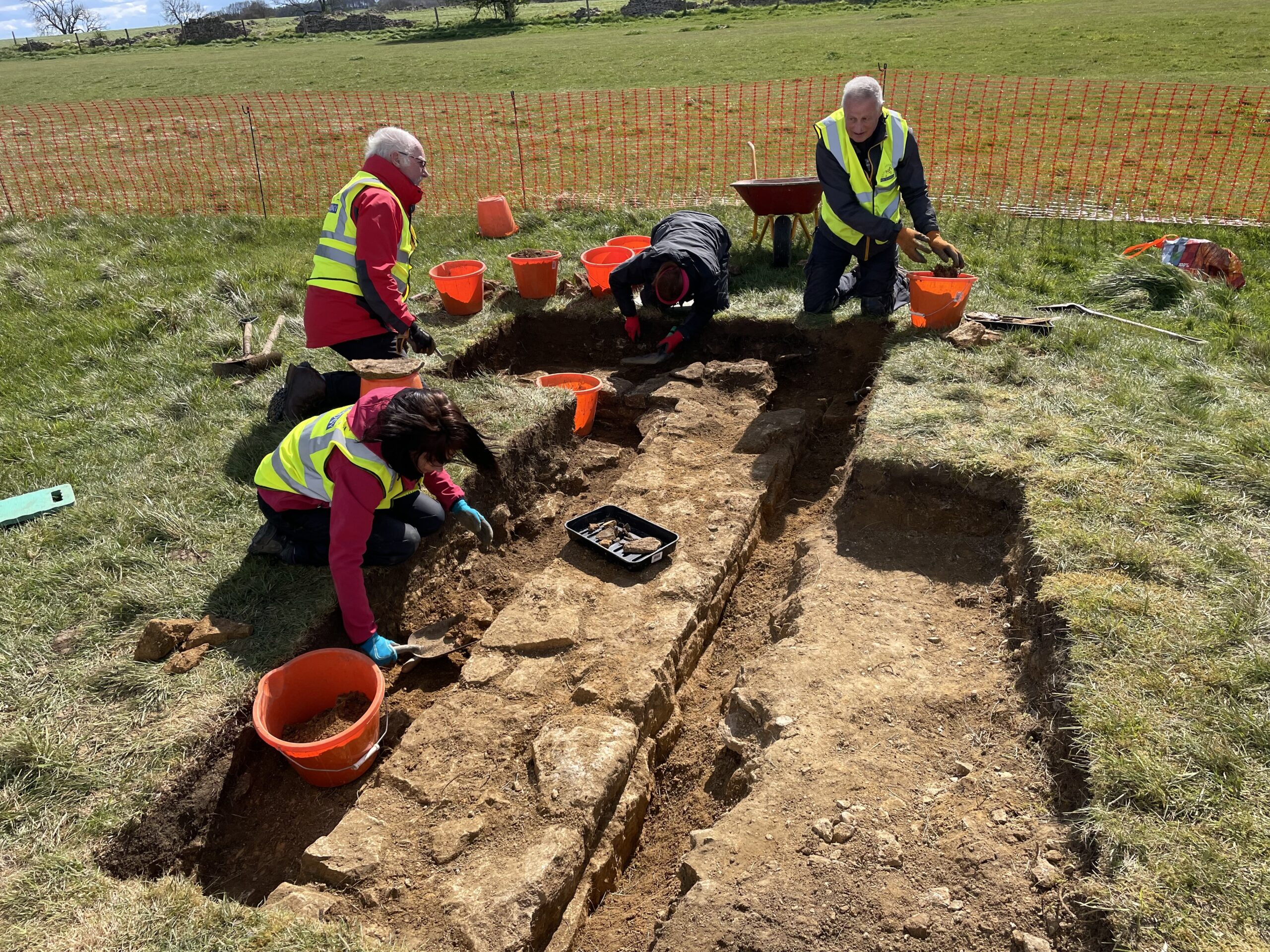
Following a successful application in conjunction with the Cleeve Common Trustee, Natural England granted permission for an excavation at the site of the grandstands of the original Cheltenham Racecourse on Cleeve Hill.
We aim to obtain a better understanding of the structure and layout of the second, stone-built grandstand and to locate the remains of the first, wooden grandstand that was destroyed by fire.
The excavation took place on 14th-15th and 19th-20th April. We found the remains of a substantial building with walls more than 0.5m thick and dimensions in keeping with the specification identified by David Aldred.
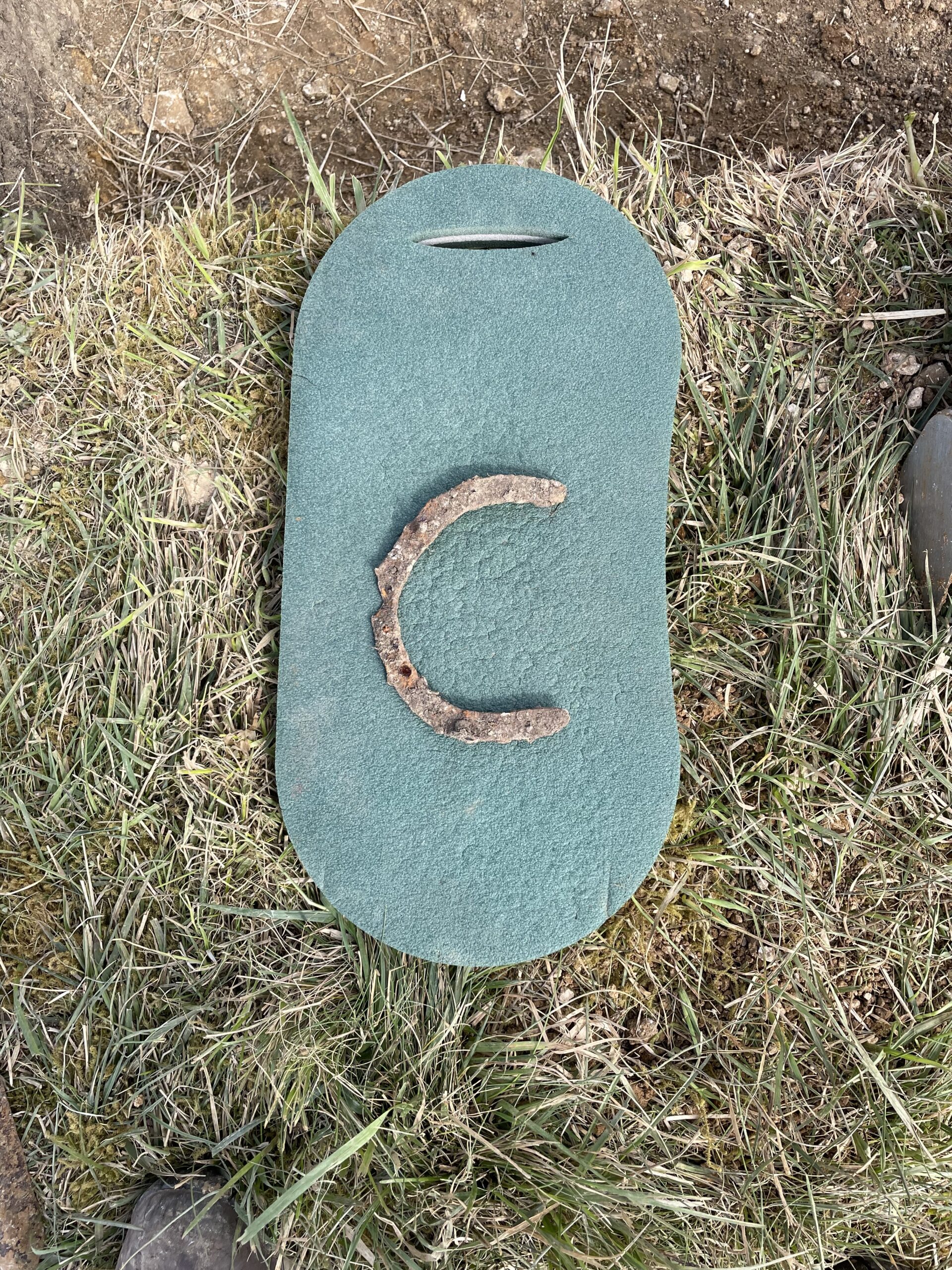
Amongst the finds was a large quantity of polished plaster, roofing slates, nails, pottery, glass, pipe stems including one with a makers mark from Shropshire, and a racing horseshoe. Once recording of the site is complete, we will backfill the trenches and return the turf. But there is still lots to explore and understand here, so we aim to be back next year.
Thanks to #cotswoldarchaeology for support surveying the site and Jamie Kyte for drone photography.
We are hoping to return to this site in the Spring 2025, subject to a permit from Natural England, which has been applied for.
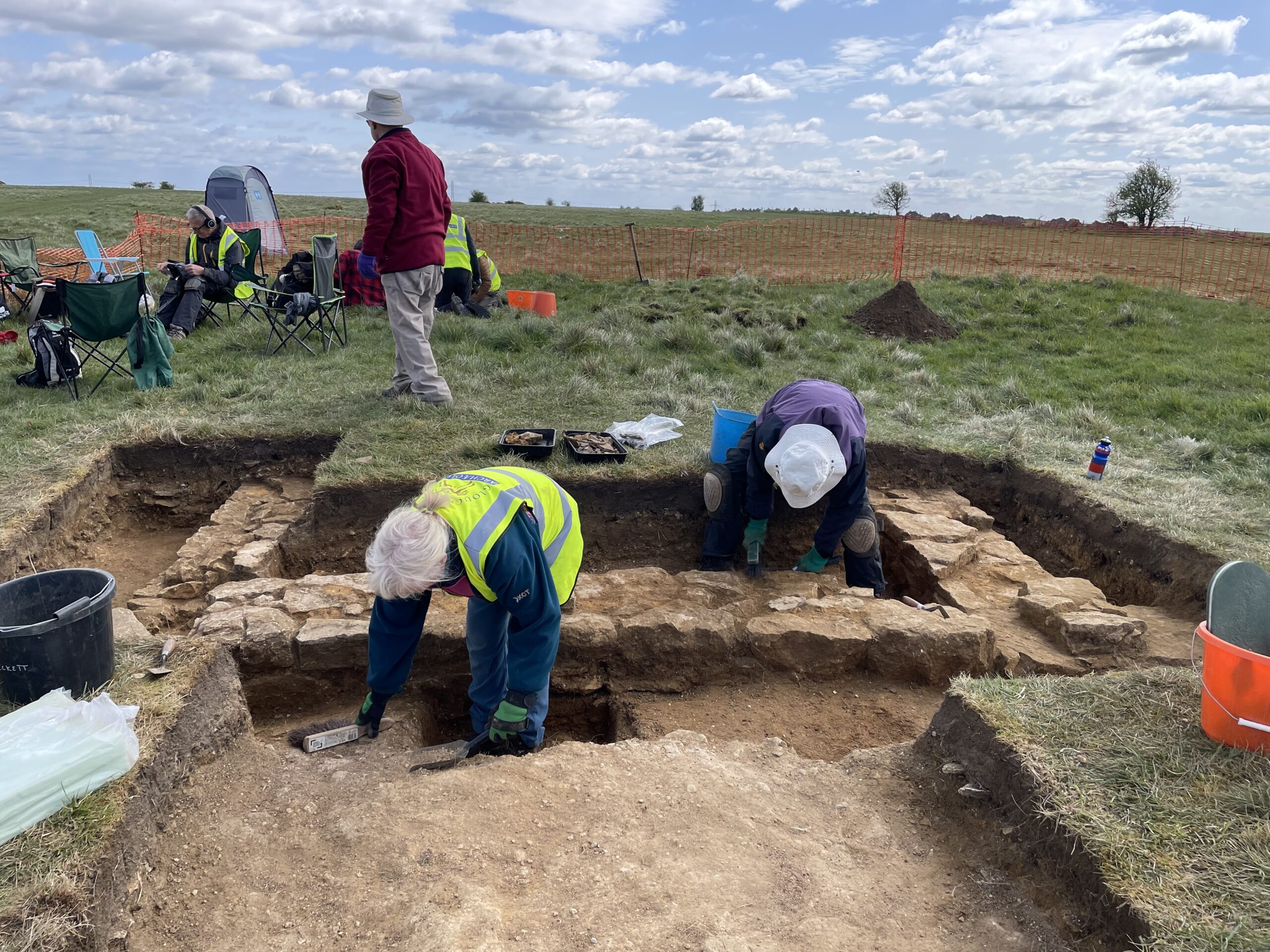






Miserden
In 2023, at the invitation of the owner of Honeycombe House (formerly Honeycombe farm and dating to the 1730’s, located near Miserden about 7 miles north east of Stroud) I was shown the site of what he believed to be a ruined building about 100m north of the current residence. The building was built onto a terrace deliberately cut into the side of a steep valley, at the bottom of which is the Holy Brook. The HER records shows a hollow way leading to the site (there is possibly a second and unrecorded one) and medieval ridge and furrow just above it.
Some buildings are shown in that location on pre-1844 maps but mid-19th C ones just show hedge lines surrounding where there used to be a building.
In June 2023, four of us decided to do a trial excavation in an area most likely to represent the remains of a wall, and quickly came down onto a well mortared stone wall with up to 6-7 courses still in situ. Pieces of plaster were still visible on the inside of the wall. It seems that the previous buildings were abandoned at some point and simply collapsed, spreading stone all over the site. It has never been ploughed and it does not appear that much if anything has been robbed away, so our hope is that the complete floor plan of the building and standing walls are just waiting to be uncovered.
Finds ranged from modern and Victorian pottery on the surface (probably kids and family picnics on the ruins!) to pottery dating back to the 14th C and possibly earlier in deeper areas, clay pipe fragments, fine glass and pre-18th C bottle glass and a whetstone. Our belief is that the precursor of the current Honeycombe house may have been in this location.
Our objectives are – to reach floor levels in a part of the main building, to collect dating evidence and to trace the complete footprint of the whole building(s) including door locations so that we can work out their use.
In 2024 we undertook 9 days of excavation at the site, revealing substantial remains of the building. A short report on the work will appear here shortly and Neil Cathie will be providing a fuller report and outlining future plans as part of the 2024-25 lecture series.
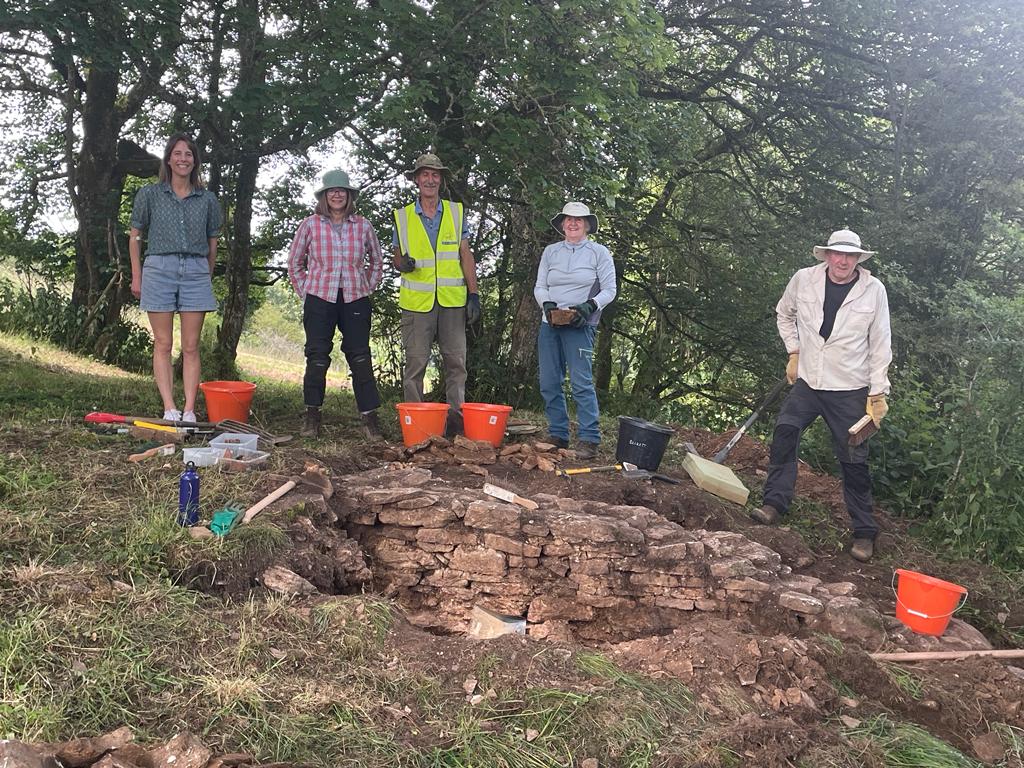
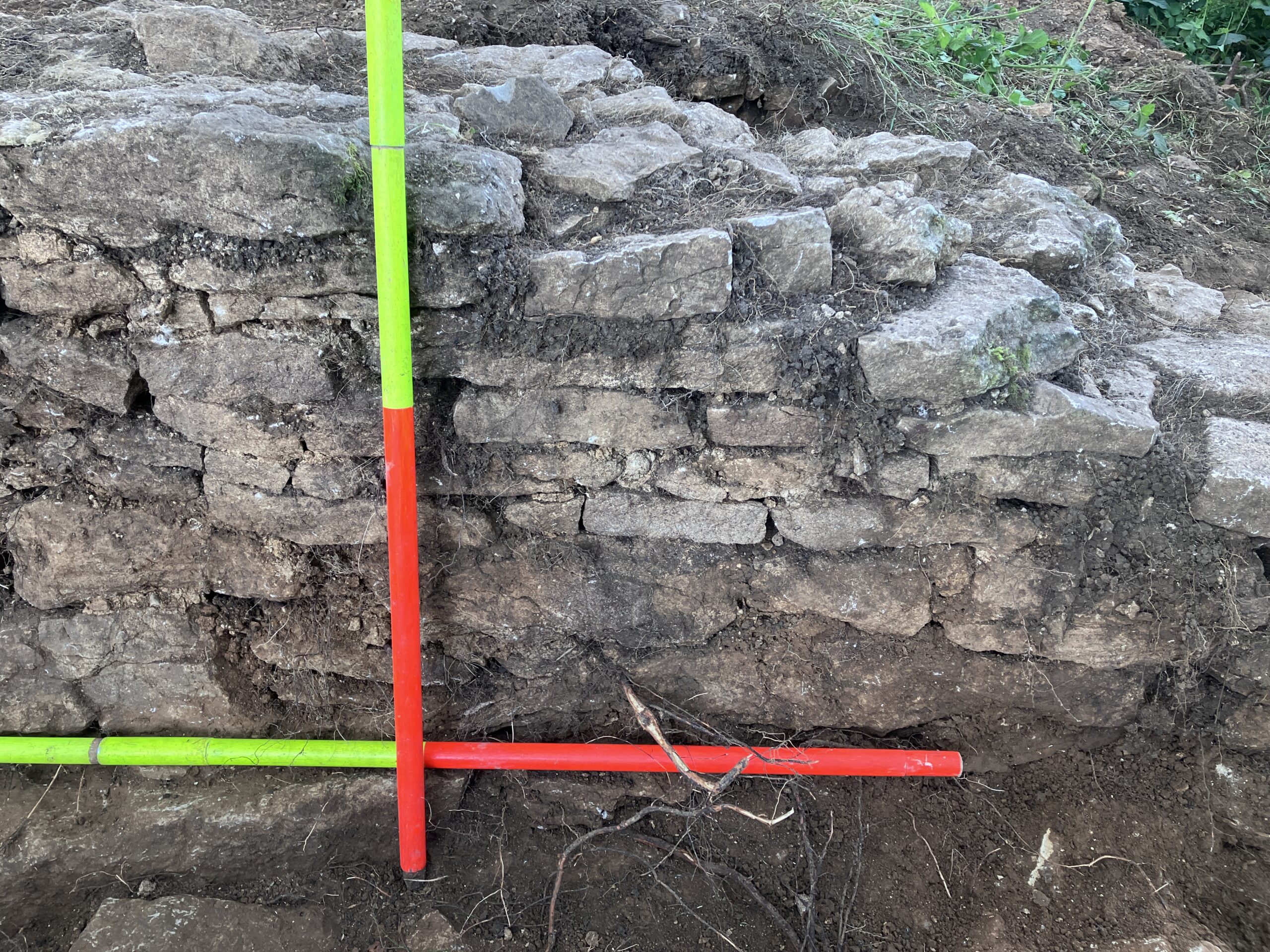


Brookthorpe
In 2021 and 2022, GlosArch volunteers, led by Neil Cathie excavated several trenches in two fields adjacent to the M5. The aim of the project is to locate the final remains relating to a Roman villa that was largely destroyed when the M5 was built in 1969.
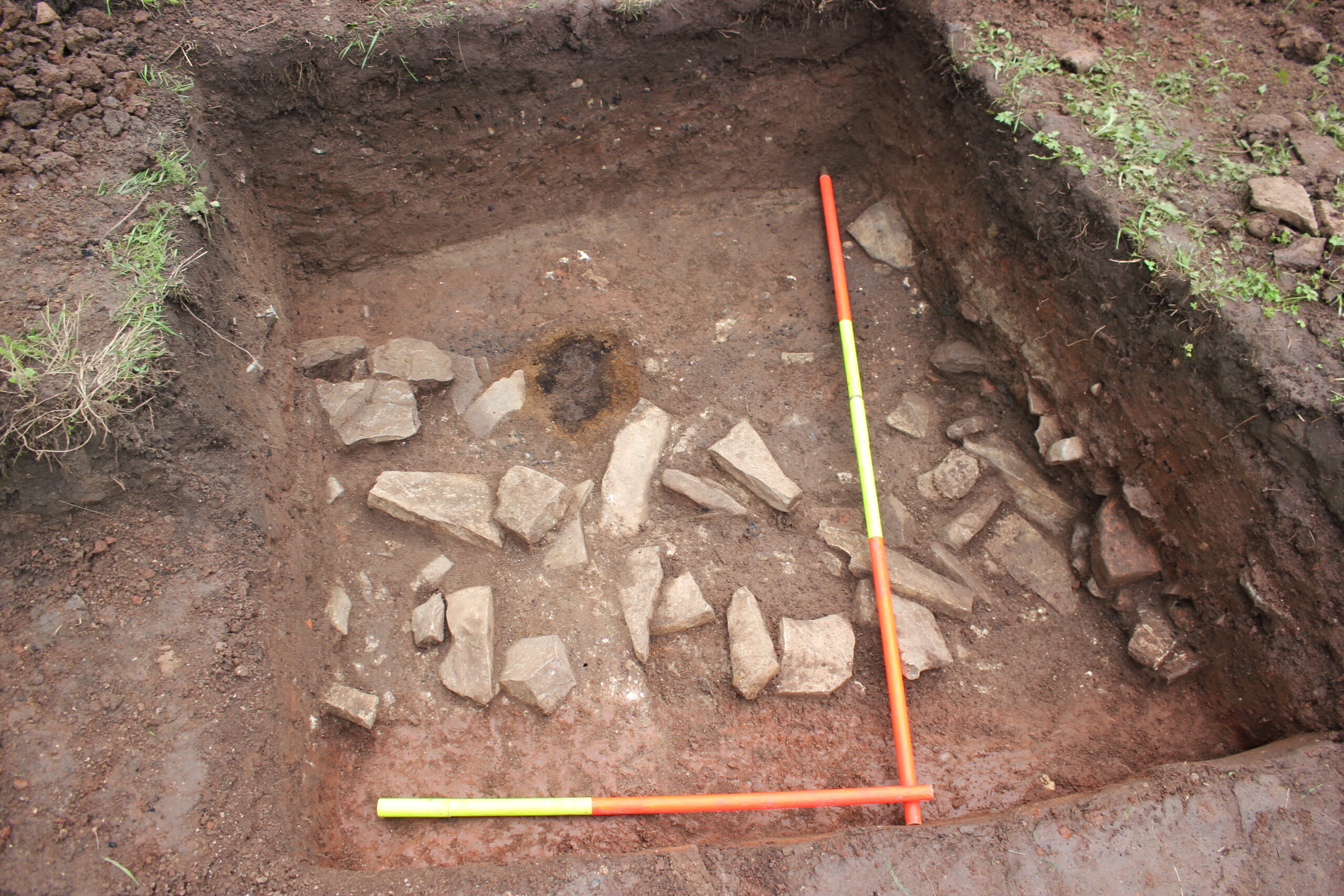
The trenches revealed substantial amounts of Roman building materials including roof tile, painted plaster and an impressive 9kg of tesserae (mosaic tiles) of six different sorts. Further excavation in very muddy conditions in November 2023 revealed further Roman material and identified an area of paved courtyard, probably relating to the villa, but no remaining walls were identified.
The interim report on the work can be found here
Severn Bank, Minsterworth
A discussion between one of our members and the landowner of this house, which borders the River Severn, led to this project to try to locate the remains of a farmhouse that is seen on a map of the village from 1757. Following resistivity and ground penetrating radar surveys in 2019, it was decided to undertake excavation to try to locate the building and understand some of the features seen on the geophysics.
Once again, Neil Cathie led the dig which placed several trenches over features seen on the geophysics. Although no building was identified, some building materials were found along with an array of pottery, nails, bone and iron ore nodules. There also appeared to be a trackway corresponding to a linear feature on the geophysics.
Subsequently LIDAR has been obtained that shows the traces of ancient hedge lines, which will enabled us to target the building more accurately.
We returned to the site in early August and identified further pottery, building materials and occasional interesting small finds which may help us to date the site. we also identified the remains of a stone wall in the expected place, and orientation, rather deeper than anticipated. The dig also saw the first outing for new tent, bought with a grant from BGAS, for which we are most grateful.
Time caught up with us again, so we are considering returning to the site during 2024.


Other Activities
LIDAR
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a way of imaging the ground using a Laser carried by an aeroplane. The Laser beam is bounced off the ground and recorded by the plane, giving accurate measurement of the height of points on the ground. When these points are put together they can create an image of thew ground surface. Since the Laser penetrates vegetation the image is not restricted by trees or shrubs covering the ground. The method has been used to locate lost cities in the jungles of central America for example.
In 2009, GlosArch (GADARG) undertook a project to assess various features of possible archaeology that had been identified along the Cotswold edge by LIDAR. Of the eight sites assessed, six showed evidence of significant archaeology, whilst at two the investigations were unable to confirm anything of significance. The results of this work have been published as “Seeing through the trees” which can be viewed here
More recently, we have employed LIDAR to investigate the hillfort on Cleeve Hill, Glos., (Glevensis 55), a site on the top of Churchdown Hill (Glevensis 54), our excavation sites at Brookthorpe and Minsterworth (see Excavations) and to locate the grandstand of the first Cheltenham racecourse on Cleeve Common. If you are interested in accessing LIDAR data for somewhere you wish to study, please let us know and we will be able to help.
Fieldwalking
This is a powerful archaeological procedure to systematically sample the upper surface of cultivated or disturbed ground, in an effort to locate or map the distribution and extent of archaeological sites. The basic assumption is made that the topsoil contains distinctive traces of archaeological activity deposited onto or into the topsoil from above, for example waste from an episode of flint knapping by someone sitting on the ground and also material from features underneath the topsoil that are exposed to the effects of cultivation or ground works and therefore mechanically brought into the ploughsoil. Cultivation will have mixed all these different sources of material together, and a proportion of what is in the soil will be visible on the surface.
Conventionally, fieldwalking in grids or along lines called transects has formed the backbone of archaeological survey fieldwork, at least where visibility is fairly good. A single researcher or team will walk slowly through the target area looking for artefacts or other archaeological indicators on the surface, often recording aspects of the environment at the time. The method works best on either ploughed ground or surfaces with little vegetation. On ploughed surfaces, as the soil is turned regularly artefacts will move to the top. Erosion and soil loss on uncultivated and lightly vegetated soil (e.g., in semi-arid environments) may also cause artefacts to ‘rise’ to the surface.
